We all have seen that there are statements in Python called yield and return. The yield statement converts a standard Python function into a generator, and users can use the return statement to end the execution and then return the output to the caller statement. This article will discuss a brief difference between generator & yield and return function in Python.
What is Yield Statement?
In Python, yield is a keyword that works like a return statement, suspending a function's execution and sending a value back to the caller. The yield statement carries on the Python function, returns its value to that function caller, and restarts from where it is left off.
Users can call the yield statement multiple times. When users call a function, and the thread of execution encounters the yield keyword within that function, the function execution halts at that line on its own.
It then returns a generator object to that function caller. When the Python function continues execution, it resumes the execution instantly after the last yield run. It lets the code generate a sequence of values over time at the same time instead of calculating them and returns them like a list.
Code:
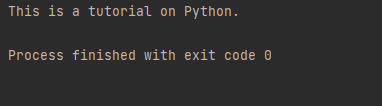
def demo1():
yield "This is a tutorial on Python."
output = demo1()
for i in output:
print(i)
Output:
Explanation:
Here, the yield prints the message provided to it and will iterate the generator object.
Another example of the yield statement is as follows:
# Here, we are coding a simple Python program to demonstrate the working of yield
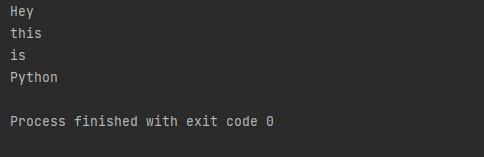
def demo1():
yield "Hey"
yield "this"
yield "is"
yield "Python"
for i in demo1():
print(I)
Output:
What is Return Statement?
Generally, users can use the return statement to end the program execution. It returns the value to the caller. The Python return statement can return all classes of values. When users do not pass an expression to the return statement, the return statement returns nothing.
There can be more than one return statement in a function, but the interpreter calls for only a single statement for any specified function invocation. 'return' statement executes only inside a function.
Syntax:
def fun():
statements
.
.
return (expression)
Code:
# Python program to
# use the return statement
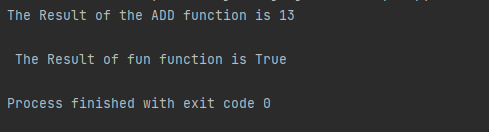
def ADD(a, b):
return a + b
def fun(a):
# It returns boolean of a
return bool(a)
# calling function
demo = ADD(5, 8)
print("The Result of the ADD function is {}".format(demo))
demo = fun(10<20)
print("\n The Result of fun function is {}".format(demo))
Output:
Explanation:
In the above code snippet, the return statement returns the function ADD by adding the two numbers.
Another example of the return statement:
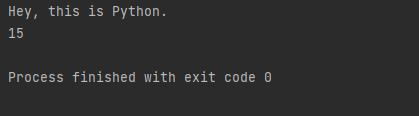
class demo: # Here, we are using a Python program to return
# multiple values from a method using class
def __init__(xyz):
xyz.str = "Hey, this is Python."
xyz.x = 15
# The fun function returns an object of the Test
def fun():
return demo()
t = fun() # Using the Driver code to test the method
print(t.str)
print(t.x)
Output:
What are Generators in Python?
Generators are functions in Python that returns an iterable generator object. The interpreter fetches the values from the generator object one at a time instead of fetching the whole list at once, and hence, if users want to get the actual values, they can use the for-loop with the next() or list() method.
Code:
Using the Generators function, we are creating generators:
def fun():
yield "P"
yield "Y"
yield "T"
yield "H"
yield "O"
yield "N"
test = fun()
for i in test:
print(i)
Output:
Explanation:
In Python, the generator function is like a general function. It will include a yield keyword instead of having a return value. When users want to create a generator function, they need to add the yield keyword.
When to use the yield instead of the return statement in Python?
Following are the reasons to use yield instead of the return in Python:
- It can drive the code to execute faster by using the yield function and is the best option when users need their execution to be faster on large data sets.
- When the data size is large, users should use the yield instead of the return.
- Users should use yield when they want to return a large set of values to the caller function.
- One of the most efficient techniques to return data is using the yield statament, as it is faster than the return statement in producing infinite or big data.
Difference between Yield and Return:
| Yield | Return |
|---|---|
| In the case of yield, the execution time becomes faster for large data sets. | Its execution time is more as compared to yield. |
| The interpreter takes no memory when users use the yield keyword. | The interpreter allocates memory for the value returned. |
| It is efficient to use the yield while dealing with large data sizes as the interpreter does not use memory. | Return is suitable for small data sizes. |
| Yield returns a generator object to the caller function. | A return within a function defines the end of execution of the Python function. |
Conclusion:
In this article, we have seen the definitions and code snippets of the yield, return, and generator statements in Python. The primary difference between the yield and return is that yield returns a generator function to the caller function while return returns a single value to that caller.