What is SPF?
Is a TXT record in our DNS stands for Sender Policy Framework (SPF).
Is an email authentication platform that prohibits unauthorized emails, people, from sending on your site's behalf. SPF may be used by an organization to publish approved mail servers.
This, together with DMARC-related metadata, notifies the recipient (or receiving systems) about the reliability of an email's origin. SPF, like DMARC, is a DNS-based email authentication solution (Domain Name Service).
As an email sender, you have the ability to choose which email servers are permitted to send an email on behalf of your domain.
If you don’t have an SPF record, your WordPress emails will likely marked as SPAM
Don’t Use More Than 1 SPF Record
Why it is required?
SPF records prevent spammers from using your domain name to impersonate you. The SPF record that you publish in DNS can be utilized by recipient servers to determine whether or not an email they received originated from an authorized server. They can then determine how to handle the email. A more detailed breakdown of SPF records may be seen here.
In recent years, SPF has gone from a "nice to have" to a "must have." Even if they aren't flawless, they are incredibly effective and an essential part of being an online email citizen. Some email administrators, however, disagree, despite the fact that without an SPF record:
- Spammers might use your domain name to distribute spam to other networks, harming the reputation of your business.
- Attackers might impersonate your domain name to perform phishing and whaling attacks, potentially resulting in ransomware, malware, and financial loss or fraud.
- Other email servers on the internet may reject your email because they are unable to validate its validity.
How to Setup SPF Record
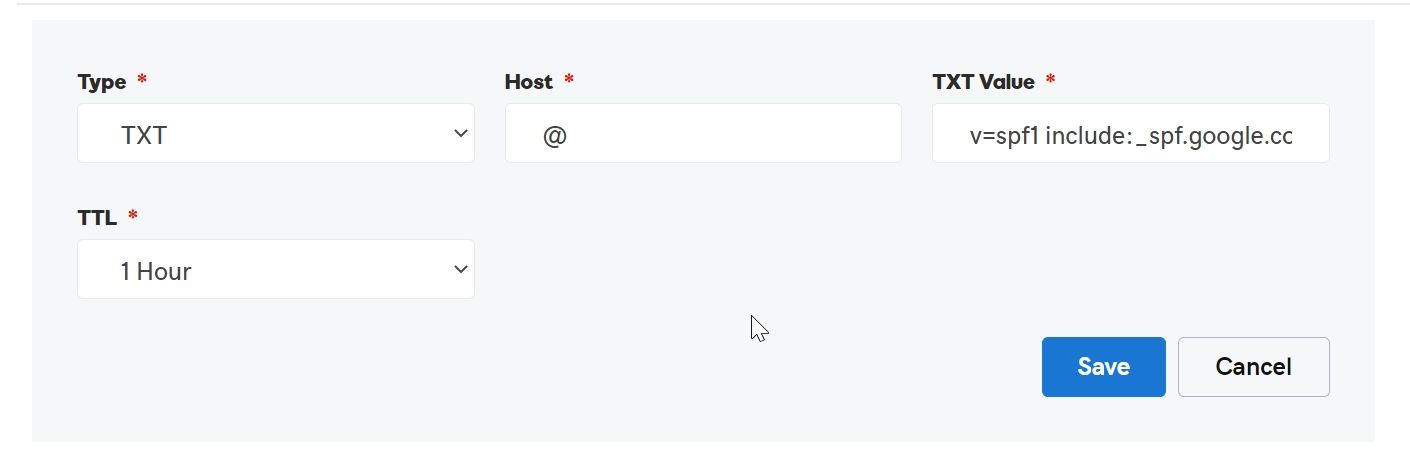
Go the DNS Panel of your Domain, create a TXT Record with value
Sample SPF record for domain yourdomain.com:
v=spf1 ip4:10.10.10.10 include:_spf.yourdomain.com ~all
| v=spf1: | version of protocol |
| Mx: | allows the domain's MXers to send mail |
| ip4: | IP network range of your web server |
| Include: | Domain include to send email |
| ~all: | It specify to “soft fail” email if received from any other domain |
SPF Record for Google mail servers
v=spf1 ip4:15.207.10.47 include:_spf.google.com ~all
SPF Record for yourdomain.com mail servers
v=spf1 ip4:10.10.10.10 include:_spf.yourdomain.com ~all
Verifying SPF records
- https://mxtoolbox.com/spf.aspx
- https://www.postmastery.com/email-audit/
- https://dmarcian.com/spf-survey/
What is a DKIM record?
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) is an email security standard that ensures messages are not tampered with while in transit between the sending and receiving servers. As email leaves a sending server, it employs public-key cryptography to sign it with a private key.
Person receiving servers using a decryption key supplied to a site's DNS to verify the message's source but that the letter's body hasn't modified while in transit. When the receiver server verifies the signature using the public key, the message passes DKIM and is declared valid.
Why is a DKIM record important?
While DKIM isn't necessary, emails signed with DKIM seem more authentic to receivers and are less likely to end up in the Junk or Spam folders. Spoofing email from trustworthy domains is a common strategy for dangerous spam and phishing operations, and DKIM makes spoofing email from domains that employ it more difficult.
DKIM is interoperable with existing email infrastructure and, in conjunction with SPF and DMARC, creates additional levels of protection for domains that send emails. Mail servers that do not support DKIM signatures can nevertheless accept signed messages without issue. It is a security mechanism that is optional, and DKIM is not a globally accepted standard.
We recommend that you add a DKIM record to your DNS wherever feasible to authenticate mail from your domain, even if it is not necessary. Postmark uses it to sign communications, while ISPs such as Yahoo, AOL, and Gmail use it to check incoming mails. We conducted tests that shown that when these security standards are used, communications are more likely to be delivered.
Another advantage of DKIM is that it allows ISPs to create a reputation for your domain over time. As you send email and enhance your delivery practices (low spam and bounces, high engagement), you assist your domain in establishing a positive sending reputation with ISPs, which increases deliverability.
DKIM record also could be a CNAME instead of TXT and point to other record which contains public key for mail domain.
How to Setup DKIM for Google email Server
Generate a DKIM key for Outgoing email using Google Admin Console
1. Login to https://admin.google.com/
Sign in using an account with super administrator privileges
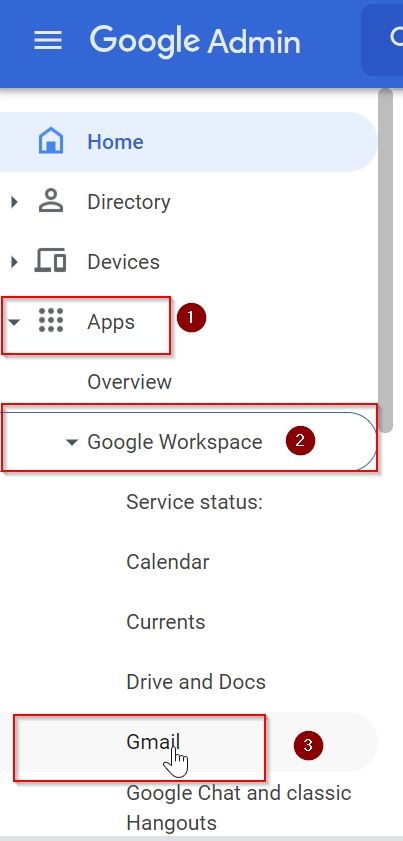
2. From the Left Navigation Panel click on APPS >> Google Workspace >> Gmail
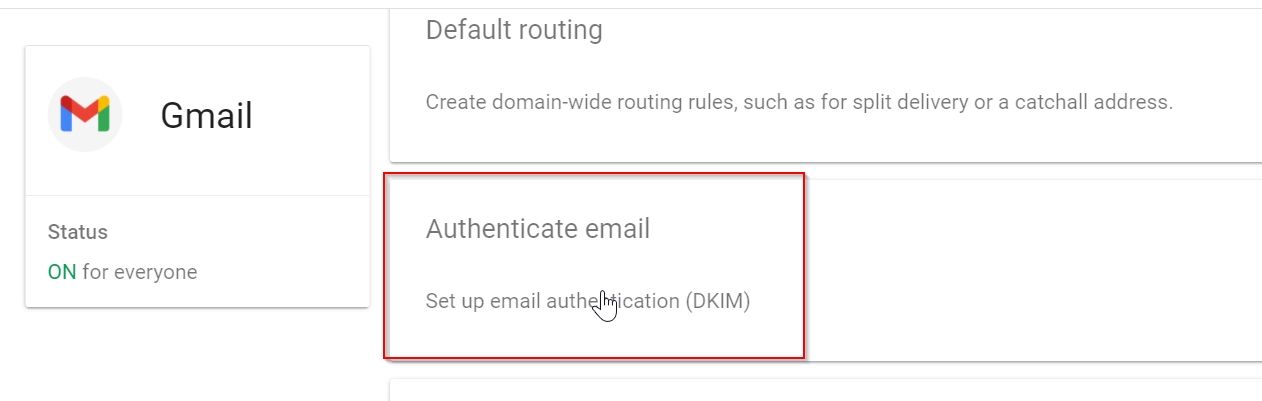
3. Under the Gmail window click on “Set up email authentication (DKIM) ”
4. Under next window click on Button “GENERATE NEW RECORD”
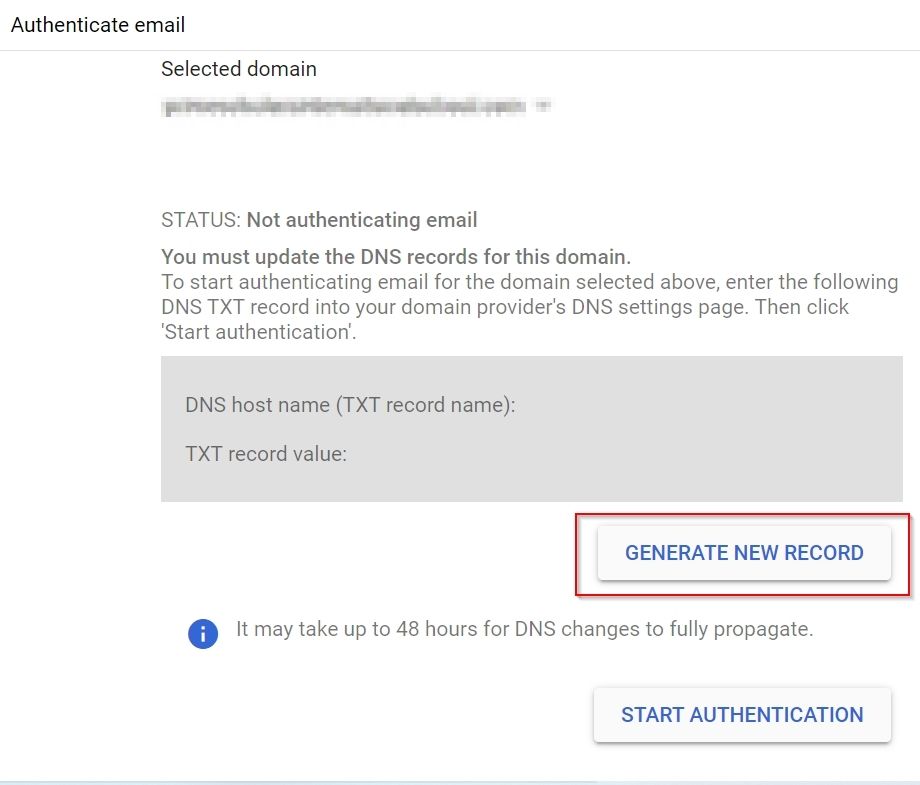
5. Under Generate New Record Window select DKIM key bit length:2048 and click on GENERATE button
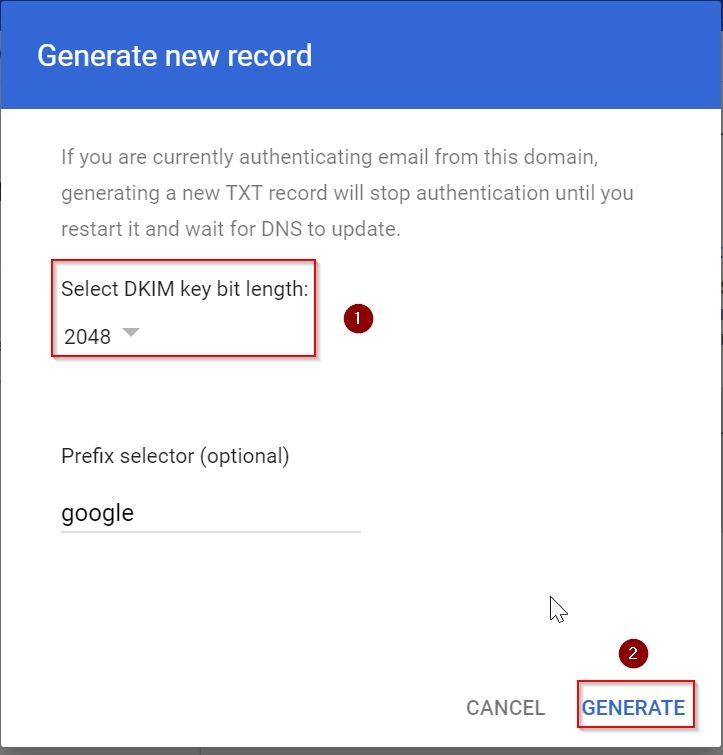
6. This will Generate a public key which you need to add in your DNS panel as TXT Record
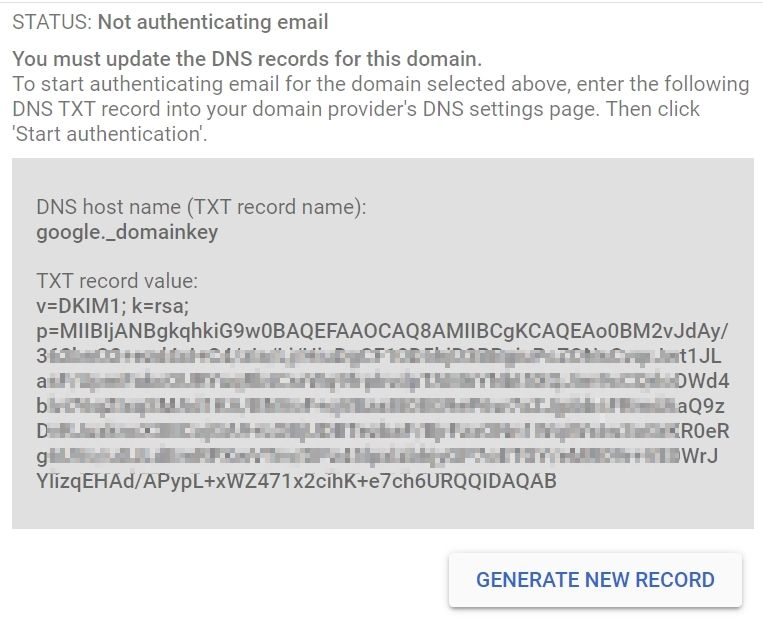
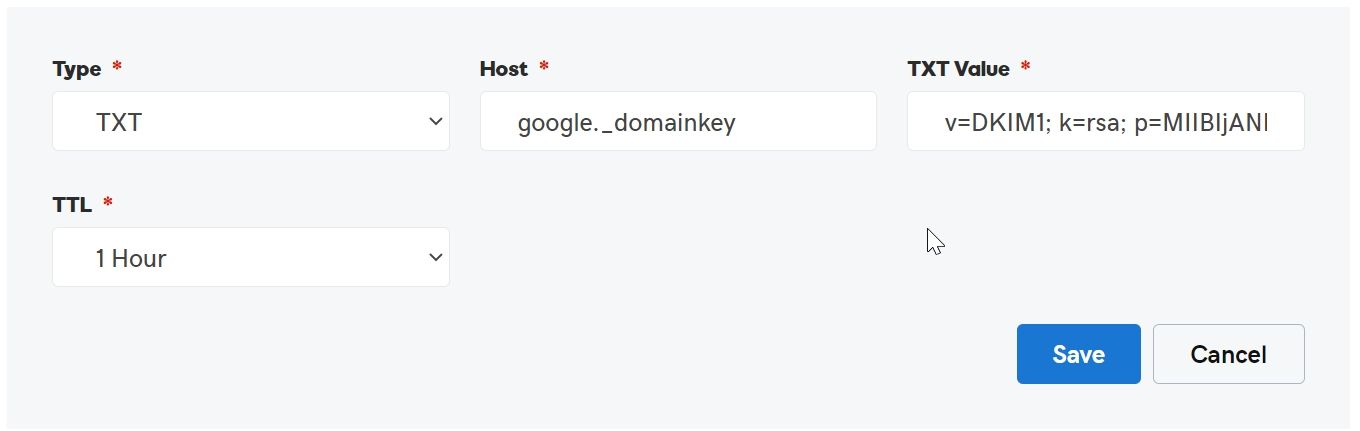
Now login to your DNS Panel of Domain and create TXT record and add given details
| Host: | google._domainkey |
| Value: | v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=”Key Value” |
Explanation:
| v: | Version of DKIM |
| k: | Encryption type |
| p: | Public key |
The given domainkey for Google email server
Verifying DKIM records
https://mxtoolbox.com/dkim.aspx
https://www.postmastery.com/email-audit/
https://www.mail-tester.com/spf-dkim-check
What is DMARC?
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) is a DNS TXT Record that may be published for a domain to govern what occurs if a message fails authentication (i.e. the receiving server cannot verify that the message's sender is who they claim they are).
A published DMARC record fulfils two functions:
- Inform the receiving server to either quarantine the message or delete it. Reject or ignore it completely Allow the message to continue its journey.
- Sends reports to an email address or addresses with information about all messages received from the domain.
Those two advantages alone demonstrate the enormous worth of configuring DMARC! When a DMARC record is published, recipient mail servers (such as Gmail or Yahoo! Mail) utilize it to determine what to do with a failed message. Gmail's receiving mail server examines the DMARC record to determine which policy to apply from the options listed below:
- Make no changes to the message.
- Keep the message quarantined.
- Ignore the notice
If the domain has published a DMARC record, the recipient mail server will take action on one of the three possibilities listed above. If the domain has not published a DMARC record, the receiving server decides whether or not to transmit the message.
Example for Domain yourdomain.com
TXT Record
| Host: | _dmarc.yourdomain.com |
| Value: | "v=DMARC1; p=reject; sp=none; pct=100; ri=86400; rua=mailto:info@yourdomain.com" |
Explanations:
| V=DMARC1 | Version |
| p=reject | Policy to apply to email that fails the DMARC test. (none, quarantine, reject) |
| Rua=mailto:info@yourdomain.com | Address to which aggregate feedback is to be send if multiple email the add comma separated email address. |
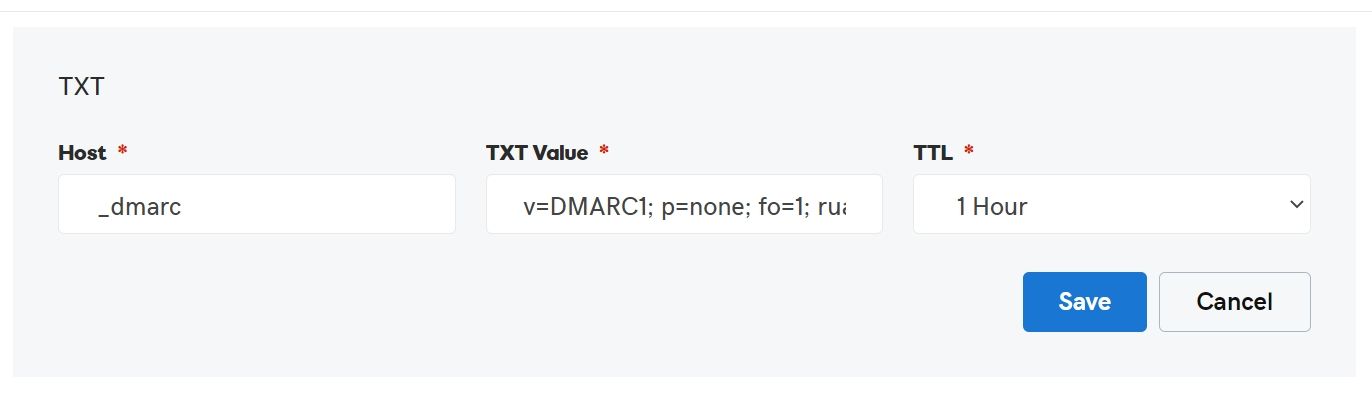
How to Setup DMARC record
Go to your DNS Control panel and create TXT record.
Verifying DMARC Records
https://mxtoolbox.com/dmarc.aspx
https://dmarcian.com/dmarc-inspector/