You might have heard about the machine learning and deep learning terminologies quite a lot. It is not because they are a part of Artificial Intelligence, but because of the capabilities, they have in training machines and building exciting models that can understand and mimic like humans. Also, when a machine is feed and trained with such algorithms, they can take prompt decisions based on the work they do. In this article, you will get a thorough insight into the differences between machine learning and deep learning.
Basic Understanding and History
Both Machine learning and Deep learning are essential parts of Artificial Intelligence. Machine learning came in the year 1950 but did not receive many endorsements. Mr. Arthur Samuel was the person to wrote the first program that can learn on its own in 1959. It was an IBM computer that went better at the checkers game the longer it played. Since then, researchers and scientists have thoughts that AI can bring revolutionary change if it can learn and train itself with every experiment it went through.
Fast-forwarding to today's scenario, Machine learning & Deep learning became the rage and a booming terminology. By the end of 2022, Gartner predicts that more than 75% of enterprises and firms will start implementing DNNs cultivating classical ML techniques. Before digging into each of these topics in detail, and their differences, let us first understand what Artificial Intelligence is?
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Often people use the words machine learning, deep learning, and artificial intelligence interchangeably to mean the same thing - but actually, they are not the same thing.
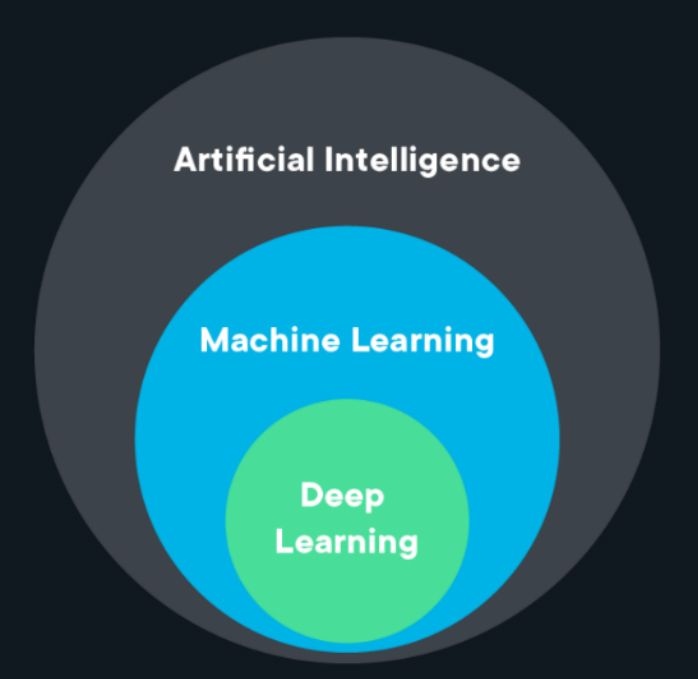
Artificial Intelligence is the art and science of preparing machines to imitate human intelligence and actions. It might sound like science fiction, but machine learning and deep learning models are drawing human and machine intelligence closer. Although, no computer or machine could completely match the complexities of human intelligence to date. The hierarchical relationship or structure of Artificial Intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning look like this.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that deals with building intelligent machines. This branch has a broad spectrum of various other subjects connected to it. This interdisciplinary domain works with distinct verticals like programming, Natural Language processing, digital image recognition, voice recognition, generic computing, neural network, computer vision, robotics, Machine learning, and Deep Learning. Now since we have understood Artificial Intelligence and its branches, let us now understand Machine learning and Deep learning one by one.
What is Machine learning?
Machine learning is an advanced applied branch of artificial intelligence that allows any machine, computer, or system to learn automatically and implicitly improve its understanding towards its goals on its own through iterated experience. Machine learning concentrates on computer program development that can feed on data and use these large datasets to learn and understand all the possible situations. These types of algorithms do not need explicit programming again and again. They are fed with structured and semi-structured data so that they can learn from these datasets.
You will be surprised to hear that almost every day, we are using the applications of machine learning - the apps we use for ordering our daily needs, the virtual assistant we use, the smart home devices we create, websites we open, and all the various technological ecosystem revolving around us are using machine learning to make themselves better for understanding their customers and users. Machine learning is the subset of AI that starts with basic observation and gradually move towards direct experience or instruction. The machine learning models help in creating an experience by extracting certain patterns out of it. These patterns, in turn, help in making better decisions as per the examples fed to them.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is the sub-branch of machine learning, where we train a machine not just to work as a human but also to mimic the internal brain functionality. This imitating of our brain neural system is called an artificial neural network (ANN). So, if you are good at machine learning and want to proceed with modeling algorithms and training them to mimic the human brain, you must have a thorough understanding of the neural network.
The neural network has multiple layers that can simulate human brain functionality. It generates patterns and serves on data to obtain machine-oriented decisions based on those neural models. Deep learning uses machine learning models and creates neural nets on top of it. Deep learning is often called Deep neural learning or deep neural network. Right from smart home devices and virtual assistants like Siri and Cortana to visual recognition devices, fraud detector systems, self-driving cars, advanced healthcare equipment - everything runs on Deep Learning algorithms and methods. These algorithms allow the machine to understand human interactions better and work in collaboration with the human.
Machine Learning vs. Deep learning:
So, now since we have understood the two popular terminologies, it is time to understand the difference between machine learning and deep learning.
| Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|
| It uses algorithms to model and train machines by parsing the data fed to it. | It constructs algorithms with multiple layers to create an artificial neural network (ANN) that runs on top of a machine learning model to make intelligent decisions as humans do. |
| It learns from the data fed to it and thus can make knowledgeable decisions. | It learns from the data but uses a neural network to make intelligent decisions. |
| Training machine learning algorithms require a smaller dataset as compared to deep learning. | Training Deep learning algorithms requires larger datasets as compared to machine learning. |
| ML algorithms take lesser time to train their models. | DL algorithms take much time to train their models as there are multiple layers of neural nets. |
| We can use the CPU to train our machine learning algorithms. GPU is not essential always. | We have to use GPU to train our deep learning algorithms adequately. Otherwise, it will either go slow or might not get accurate modeling. |
| Training ML models are less time consuming. | Training DL models need more time and effort. |
| The output that gets generated during this process is mostly in numerical form. | The output that gets generated during this process could be in any form, including free form elements like free text and sound. |
| Reinforcement, supervised learning, and unsupervised learning are examples of machine learning methods. | Creating neural networks, deep neural nets, and artificial neural nets are methods and tools used for creating deep learning models. |
| Machine learning helps in providing insights based on the data fed to the models during training. | Deep learning helps in providing decisions as humans do, based on the models trained during the creation of artificial neural nets. |
| Machine learning mimics human work and operation techniques. | Deep learning mimics the human brain and cognitive abilities to make prompt decisions. |
| Machine learning is the super set of deep learning. | Deep learning is the sub branch of machine learning. |
| Machine Learning evolved from AI. | Deep Learning evolved from Machine Learning itself. |
| Machine learning requires thousands of data points. | Deep learning requires millions of data points that Big Data provides. |
| Data scientists design these ML models to function and predict future action from data. | Data scientists design these DL models so that machines can have the cognitive and decision-making abilities as humans do. |
| Data analysts design and detect the algorithms to examine specific variables from the data set. | Data, in this case, gets self-depicted on analysis and put into production. |
| The primary purpose of Machine learning is to find insights, look for competitive outcomes, and learn new things. | The primary purpose of Deep learning is to solve new problems, find new knowledge & decision-taking approaches. |
| Companies use machine learning in search engines, filtering spam messages, detecting unusual transactions, finding insights and sales predictions, etc. | Companies use machine learning in creating virtual assistants, robots that mimic human work, autonomous vehicle systems, object detections, creating intelligent medical equipment, smart home devices, etc. |
| Training ML models need lesser GPU utilization. | Training DL models need more GPU utilization. |
Conclusion:
Machine learning & deep learning will transform our lives for generations to come. Almost all industries will experience transformation with the implementation of ML and DL capabilities. Sedate engineering techniques and jobs like space travel and working in hazardous environments will be performed via machine involvement mimicking human workflow. The possibilities of Machine learning and Deep learning involving every industry are growing exponentially. Also, the scope of jobs and career opportunities in these fields are expanding rapidly.