RAM and ROM
In a computer, the internal memories are RAM and ROM. The full form of RAM is Random Access Memory, while the full form of ROM is Read-Only Memory. This article aims to throw light on the differences of RAM vs. ROM in tabular form. You will also get to know about the types of memory in computers, types of RAM, and types of ROM. What follows will enable better usage and understanding of these vital computer parts. Read on for more!
RAM vs. ROM
| RAM | ROM |
|---|---|
| The stored data is non-permanent. It can be modified, written, or deleted any number of times. | The stored data is permanent. It can be modified at prolonged speed and only a limited number of times. |
| It comprises of high-speed memory. | ROM is slower than the RAM to a large extent. |
| The CPU is capable of accessing the data stored on it. | The CPU is incapable of accessing the data stored on the ROM. The data has to be transferred to the RAM before the ROM can access it. |
| Large-sized with higher memory storage capacity. | Smaller in size than the RAM and has lesser memory retention and storage capacity. |
| Usage of RAM: Primary memory comprises DRAM DIMM modules and CPU Cache (SRAM). | The usage of ROM: In firmware such as BIOS and UEFI. Microcontrollers, RFID tags, medical devices, as well as in devices wherein permanent memory solutions are necessary. |
| Quite expensive. | Relatively inexpensive. |
| RAM is a read-write memory | ROM is a read-only memory |
| RAM stores the temporary data that is being processed by the CPU currently. | ROM stores instructions needed during the bootstrapping process. |
| Ranges from 64 MB to 4 GB. | ROM is comparatively smaller in memory size. |
| They are classified into Dynamic and static RAM. | Classified as PROM, EPROM, and EEPROM. |
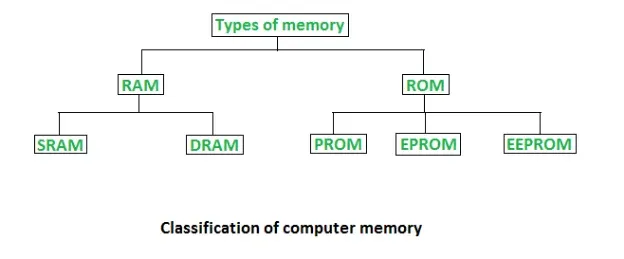
Types of Memory in a Computer:
Computer memory is basically of two types –
1. Random Access Memory (RAM) which is the primary internal memory of the computer and is volatile.
2. ROM meaning Read-Only Memory or the second internal memory of the computer is non-volatile.
Ram and Rom are further divided into SRAM and DRAM, and PROM, EPROM, and EEPROM, respectively. These sub-divisions of RAM and ROM are discussed in the following paras.
What is RAM?
RAM or Random Access Memory is the largest internal memory unit in a computer. It is second only to magnetic hard drive or SSD in terms of memory storage capacity. RAM comes in use for storing all the data that is generated and used by the Central Processing Unit of the computer in real-time. Unlike ROM, the data on RAM is capable of being read, edited, written, and deleted as many times as needed.
As RAM is volatile, any data stored on it will disappear as soon as the power supply is cut off. This is the primary reason why the RAM cannot be used as a permanent storage device even though it provides much faster access than magnetic disk-based HDDs. Given the volatile nature of the RAM, the processed data has to be saved on the HDD to avoid any data loss in case of a power cut or an unexpected system shutdown.
Types of RAM
RAM can be classified into two distinct types:
1. SRAM (Static Random Access Memory)
2. DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
Static RAM or SRAM needs constant power flow to retain the data within. More expensive and faster than DRAM, it serves as the cache memory of a computer. On the other hand, Dynamic RAM or DRAM has to be refreshed for retaining the data within. It is cheaper and slower than SRAM.
Differences between SRAM and DRAM
What is ROM?
ROM or Read Only Memory is defined as an internal memory of a computer. As evident from its full form, the data on the ROM can only be read by the Central Processing Unit of the computer. It cannot be modified or changed in any way. To access the data stored on the ROM, the CPU has to go via the RAM. The data on the ROM is first transferred to RAM, and only then can it be accessed by the CPU.
ROM is a storehouse of the instructions received by the computer during the bootstrapping process or the booting up process of the computer. As ROM comprises a non-volatile memory, the data stored on it will remain intact even after the CPU is switched off. As the capacity of reading Only Memory is lesser than that of Random Access Memory, it is cheaper and slower than the latter.
Types of ROM
There are three types of ROM:
1. PROM: Programmable ROM - PROM can be modified just once by users.
2. EPROM: Erasable and Programmable ROM – The data present on EPROM is capable of being erased with the help of ultraviolet rays. It can be reprogrammed.
3. EEPROM: Electrically Erasable and Programmable ROM – EEPROM is capable of being reprogrammed after being erased electronically (about 10000 times).
Conclusion
RAM and ROM are essential and necessary internal memory units for the computer. RAM is significant for CPU processing. ROM is vital for the computing unit to boot up. The ROM is equally essential and can be found on removable storage media devices like USB drives, Solid State Drives, SD cards, etc. – these are instances of the advanced implementation of EEPROM, a classification of read-only memory.
We have outlined essential differences between RAM and RAM above. In case you come across any other distinction between RAM and ROM then do leave a comment below, we will be waiting to hear from you.