Serial Transmission witnesses a series of data being sent one bit at a time wherein every bit follows another. The transmission that ensues is of two types - synchronous and asynchronous.
This article aims to throw light on what is the synchronous and asynchronous transmission, how they differ from each other, etc.
Synchronous vs. Asynchronous
| Basis of Difference | Synchronous | Asynchronous |
|---|---|---|
| State Variables | Universal clock signals are used for synchronizing the changes in state variables. | There is no synchronization for state variables to change simultaneously. These variables may change at any given time and regardless of each other. This change leads to the achievement of the next steady internal status. |
| Degree of reliability | As all changes in the Internal State happen to be under the strict control of the master clock source, the likelihood of failure is much less. The probability of a race condition is also less, and so this type of transmission is more reliable. | The absence of a universal clock source in asynchronous transmission impacts its internal state changes. As and when the inputs change, the results become more prone to race-like conditions. |
| Transmission of data | Data is sent in the form of frames or blocks. | A single byte or character is transmitted at any given time. |
| Timings – Internal state changes | The timelines of internal state changes are in the control of users. | The changes belonging to the internal state of asynchronous circuits fail to be within the control of users. |
| Speed of transmission | The transmission speed is breakneck. | The transmission speed is slow. |
| Costs to user | Transmission of data through synchronous means is costly. | The transmission of data via asynchronous methods is comparatively economical. |
| Interval of time | The time gaps in synchronous transmission serve to be constant. | The time gaps in asynchronous transmission are randomly selected and keep changing with time. |
| Gaps between data packets | There are no gaps present within the different packets of data as they get transmitted from their origin to the destination. | Gaps are present in between two data packets. |
| Instances | Video Conferencing, Chat Rooms, Telephonic Conversations, etc. | Emails, forums, letters, etc. |
What is Synchronous?
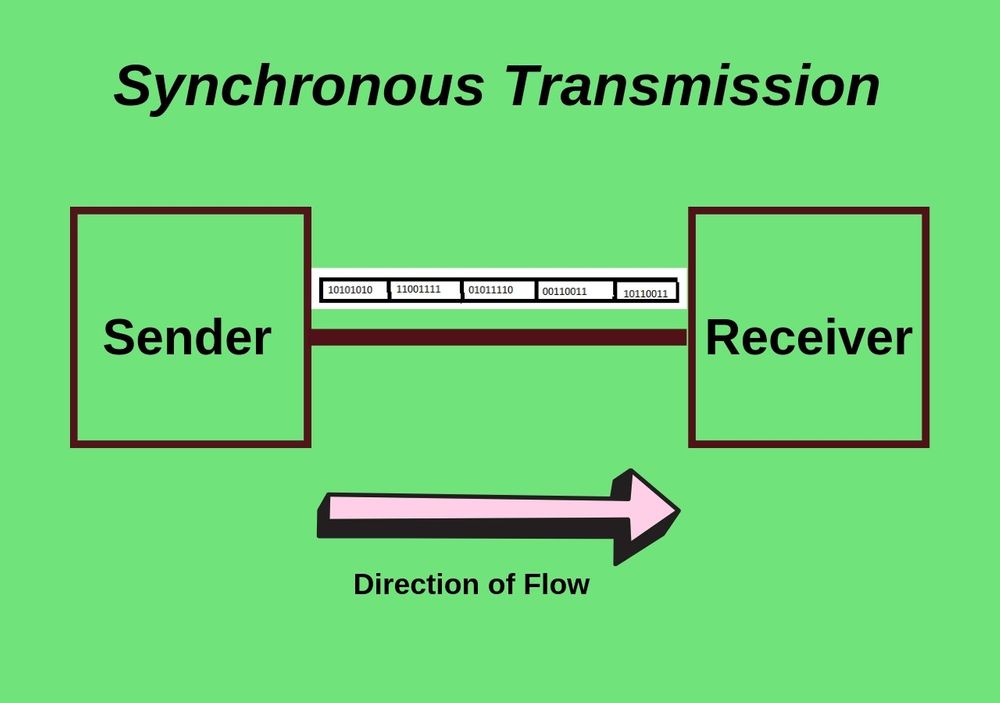
Synchronous Transmission relates to data flows following a full-duplex mode. This duplex mode comprises of blocks or frames. In this type of transmission, synchronization between the receiver and sender becomes necessary; therefore, the sender is aware of where any new byte starts as no gap exists between any two data packets.
Synchronous Transmission serves to be reliable, efficient, and useful for passing on large data volumes. It offers real-time communication to link up connected devices. Some essential instances of Synchronous Transmission are Video Conferencing, Chat Rooms, telephonic conversations, face to face interactions, etc.
What is Asynchronous?
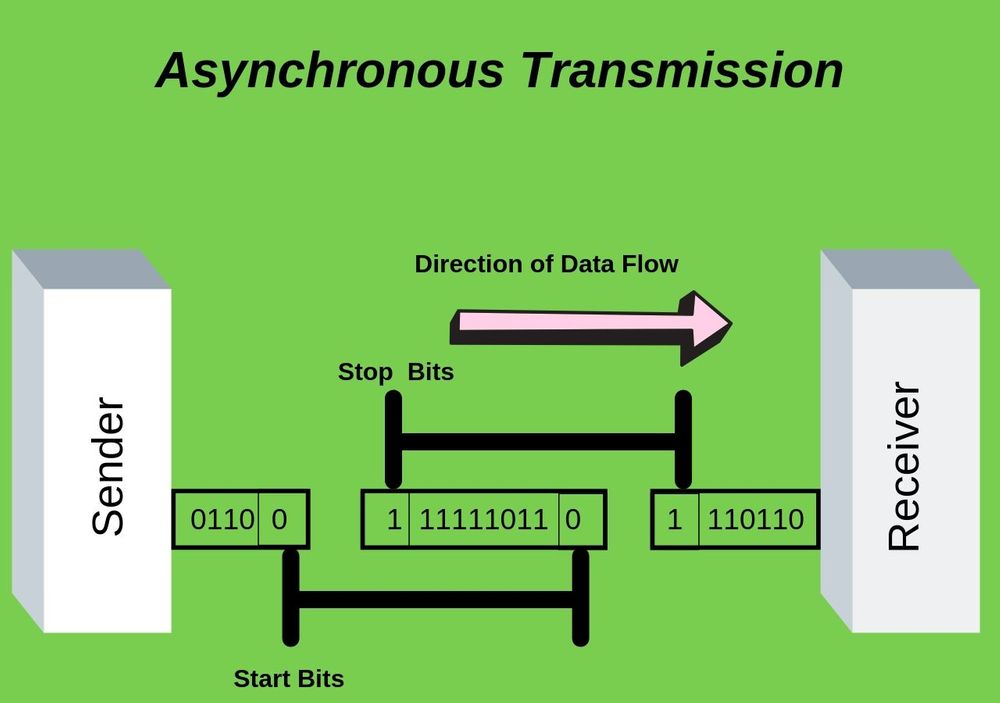
Asynchronous Transmission refers to data flow occurring in half-duplex mode – in the form of a single byte or character at any given time. The data transmission takes place as a consistent and continuous flow of bytes. Typically, the size of characters being transmitted is 8 bits to which parity bits (stop and start bits) are added to become a total of 10 bits.
Asynchronous Transmission does not need a clock for synchronization purposes. On the other hand, it utilizes parity bits for letting the receiver understand how to interpret and receive the transmitted data. It is a fast, economic, simple means of transmission that does not rely on 2-way communication. The famous instances of Asynchronous Transmission are emails, forums, letters, televisions, radios, etc.
Key difference between Asynchronous and Synchronous
- In the case of Synchronous Transmission, the data gets transferred as frames; on the other hand, in the case of Asynchronous Transmission, the data transmission takes place in the form of a single byte at any given point of time.
- Synchronous Transmission makes the inclusion of a clock signal a necessity. It links up senders and receivers with the intent of providing information to receivers for any new byte. Conversely, in the case of Asynchronous Transmission, the sender and receiver do not need clock signals. This is because the data sent through this means has parity bits attached to the same and showcases the beginning of any new byte.
Conclusion
Asynchronous and Synchronous Transmission possess their pros and cons. They have to be used in line with the immediate requirements of the sender and receiver. In case you have any further queries with regards to Synchronous vs. Synchronous Transmission then do get back to us in the Comments section below, we will be happy to assist you!