Talent Management System is the best technology in the field of HR and for the roles of HR professionals. HR stands for Human Resource, a department under an organization charged with exploring, finding, filtering, recruiting, providing internships to job applicants, and administering benefits.
Talent Management Systems, commonly termed TMS by HR professionals, is a set of software applications that helps charge the management system of recruiting talent, qualifying candidates, and retaining human capital within an organization. This article will provide a descriptive idea of how TMS works within an organization.
What is Talent Management System (TMS)?
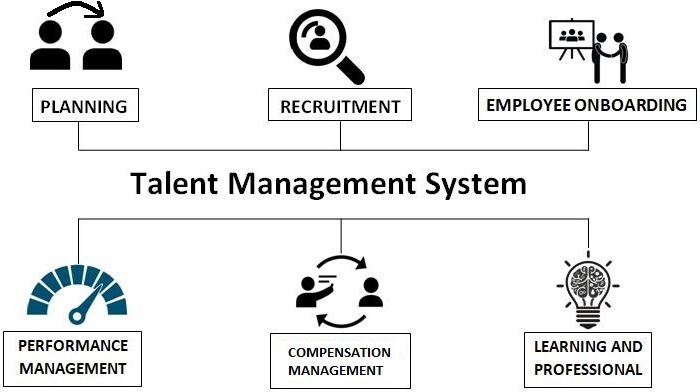
A talent management system, or TMS, is an integrated software suite that helps manage and supervise core talent systems. It includes recruitment, job applicant onboarding, performance administration, learning and professional development, payment management, and masterminding succession plans.
These techniques, and the technical faculties that support the organization's HRs, are generally delivered through these software modules. So, businesses can trigger what they require for their development and add extra functionality as they grow.
As we know, every organization has a department that manages job recruitment and retention of employees. Dr. Anthony Barker and his team first introduced the Talent Management System (TMS) to maintain track of talent within an organization. An organization classifies talent as valuable members of personnel and future employment prospects who have applied for open job posts.
Today, prominent and mid-sized businesses use the best TMS that helps maintain records of data at many different points in the personnel life cycle.
If an applicant plans on working in the developing field of TMS, they will need to understand how to navigate through a TMS system and use the whole system as they scope out, qualify and recruit talent.
The Evolution of the Talent Management System:
Talent management evolved into one of the most popular talent management for an organization's entire workforce and not just top-level associates and high potentials. Talent management technology strives to offer HR teams a way to facilitate hiring processes and gain a thorough understanding of their workforce globally.
Many such platforms have the self-service capability that allows staff and workers to access, edit and update information. It takes away the admin burden from the Human Resource (HR) department.
Let us discuss the evolution of TMS and understand why Talent Management has developed and evolved into such a vital management system:
The First Phase: The Personnel Department:
By the 1970s and 1980s, the hiring process responsible for job applicants was known as "The Personnel Department." The role of this group was to find, screen, recruit, train job applicants, and pay them with their salary, and they had the required benefits. The systems which extended up to sustaining these processes were batch payroll systems.
Advantages of the First Phase:
- Organizations understand the advantages of using TMS technology to handle HR administrative functions.
- These systems handle transactional issues and help capture basic employee information for record-keeping.
Disadvantages of the First Phase:
- Transactional systems do not support finding, aligning, measuring, or managing the workforce.
- It limits the reporting to the center Human Resources. Reporting HCM functions are manual to a certain extent.
The second phase: The Strategic HR:
By the 1980s and 1990s, organizations discovered that the HR function was more crucial, and the notion of "Strategic HR" arose. At this time, organizations realized that the Vice President of Human Resources had a much more significant role. They recruit the right people, train them, and help the business create job roles and organization structures (organization design).
They also develop "total compensation" packages that incorporate stock opportunities, benefits, and compensations and serve as a central part of communication for personnel health and happiness.
The "Head of Personnel" became the "Vice President of Human Resource" and had a much more crucial role in business processes and functions. The organizations that built up these systems to support this new role include finding, hiring, total compensation systems, Applicant Tracking System (ATS), and learning management systems.
From this role, today, the HR department has developed into a more significant role than a business function. It is a business partner of an organization reaching out to assist lines of business within that organization.
Advantages of the Second phase:
- In this phase, the system automates the processes to improve efficiency, productivity, and lower expenditure.
- A new breed of Human Capital Management (HCM) applications automates typical business processes.
- Administrators can now view reports on hiring and performance management tasks.
Disadvantages of the Second phase:
- The overall systems are still diversified and unintegrated.
- The advantages of this phase come from single-point process automation and not alignment with general business objectives.
- In this phase, the system confines the reporting to typical HCM processes that retain no capability to report on or scrutinize data across systems.
The Third Phase: Integrated HCM Processes and Talent Management Suites:
With the advent of the Talent Management System (TMS), it was border lining up to hiring job applicants and paying their salaries. But we are now stepping into a new era, called the emergence of "Talent Management." HR and L&D organizations are now concentrating on a new set of strategic points.
In the third phase, organizations start turning to application providers for companies of HCM applications or talent management suites. Regardless, with best-of-breed providers developing and loosely connecting additional applications, it manages to reside the information in multiple locations.
It thus requires more number of inputs and lacks a single sign-on. Companies that desire to achieve the fourth phase in the Talent Management Maturity Model need a broad view of applications and talents built to unify their talent management functions.
Advantages of the third phase:
- This system automates multiple Human Capital Management (HCM) processes.
- The system involves the integration standards between HCM and HR systems.
- Talent management suites are being initiated.
- The user interface is improved to enable widespread adoption.
- Analytics and reporting are improved to retain individual talent management processes.
Disadvantages of the Third Phase:
- No consolidated insight of workforce talents and competencies.
- Since the information of the management system resides in multiple databases, the reporting across talent management functions is restricted.
- The system holds no power to transfer talents across the business.
- The whole processes remain disorganized.
The Fourth Phase: The future of the Talent Management System:
The future of Talent Management initiates with the fourth phase. In this phase, the management system designed the processes and applications to guide business performance through a unified view of talent reviews. The aim is to achieve business plans to find and fill talent gaps.
Without cooperative recruiting and undertaking, it is challenging to identify talent gaps that need more proper understanding through training versus internal mobility or recruiting external talent. The goal of this phase is not confined to the point that the system will attract new talent but also to estimate and analyze what talent the organization will need.
The technology also determines whether an organization or business should internally develop the talent or recruit them from the outside. Based on the demands of an organization's departments and business, this system also determines when and where they need to apply talent.
These plans require focusing on the applications and processes that represent the shifting from the third to the fourth phase in talent management.
Advantages of the fourth phase:
- The technology renders a systematic view of talent management.
- It eradicates double entry of data.
- Declines costly integration.
- One of the most significant points is the technology uses mechanisms and configuration for ease of use and widespread adoption.
- Through systematic reporting and analytical opinions across talent systems and businesses can drive alignment and promote organizational performance.
Disadvantages of the fourth phase:
- High-level management responsibility within a corporation is yet lagging behind systems development.
Benefits of Talent Management Solutions within an organization:
Organizations with efficient and practical talent management are more feasible to beat opponents, and public corporations with a verified talent management initiative even offer higher shareholder returns than most other corporations.
Here is a list of the top five significant benefits of a Talent Management System (TMS) for companies and their employees:
Recruitment Process:
There is always a competition for specific job roles that require qualified talents. Organizations or businesses must own efficient processes and technology that help with sourcing, workforce management, applicant tracking, and analytics to hire applicants for such positions and make an agile recruitment process.
Lapse in communication with skilled candidates and lagging due to the lack of proper tools and technologies to push the top applicants through the recruitment process can affect the ability of HR to hire the best employee.
Recruiting software helps organizations track and manage applicants and provide an easy method to see where they are in the hiring procedure. It allows recruiters to source and find the applicants who applied through various hiring platforms. It also provides an efficient way for feedback on those applicants.
1. Better Planning during Recruitment:
Every organization has employees with senior roles who hold technical knowledge and expertise in a specific branch. Without a standardized system for communicating with senior employees and transferring their knowledge, the business can reach a spot where it will find no succession planning and decrement in the organization's growth.
Very few organizations have a systematic and formalized succession planning system. They lag due to the incapability of transferring the knowledge of the retired people or those senior employees who will leave the organization.
A Talent Management System can assist with succession planning by utilizing data to envision bench strength for employees prepared and willing to move on to advanced roles, map skills to available job positions, identify vacancies and add applicants with qualified skills.
2. Own Top and High-qualified Talent:
This advantage is one of the most crucial points for an organization to hire a qualified applicant. Once they hire the best employees, they need to keep them. With all the data and information of the employees hosted on a single platform and neatly systematized into an online profile, they can keep records of their performance reviews, skills, goals, and career aspirations. It helps them confirm that their employees are satisfied and are working on the right track. Keeping a TMS in its proper workings within an organization to collect all the data makes it easy to explore, analyze, and informs which employees need event promotion, training, development, and monitoring.
3. Increased employee and manager engagement:
If an individual is looking to improve engagement in their company, enforcing a TMS can help. An employee profile entrusts managers and employees to interact with an employee's professional career succession. An integrated TMS solution promotes the workforce to invest in the organization and align their daily work with the business plans while concentrating on their personal goals.
4. Increased Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DE&I):
DE&I offer businesses a strategic and financial benefit. It is becoming a central focus for candidates as they job hunt. Diverse workforces boost employee creativity, knowledge, sense of belonging, and fulfillment in work, which brings positive business developments.
5. Improved onboarding experience:
A systematic, seamless, and efficient strategy for onboarding is achievable using the TMS. Recruiters can create applicant profiles that hold all the data and information assembled during the hiring and recruitment processes.
6. Improves employee experience:
We all know that employee turnover is a matter that every organizational workforce avoids at all costs. A TMS that incorporates payroll improves the employee experience by authorizing access to holiday requests, payslips, and management of sick leave. They can also include organizational charts that help employees understand the management and reporting setup of that company.
7. Improves performance management:
Talent management software can enable organizations to move to dynamic performance administration, where feedback is more open and straight between the manager and the employee. Only about one-quarter of employees say they have received feedback that improves their work.
It admits that employees desire feedback but that much of what they receive is not that valuable. Feedback attempts to provide them with the pieces of information that will help them improve their flaws and further grow their skills.
Talent Management System market:
The extent of the Talent Management Software market is vast. It has been segmented depending on organizational size, component, and deployment. The system divides the deployment part into on-premise and cloud-based platforms.
The increasing penetration rate of cloud-based platforms, including the approval of mobile-based personnel management systems, is one of the critical factors driving the market growth. Organizations and Human Resource experts are increasingly adopting Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms for automated searching, placing, and hiring new talents from the job applicants group and keeping the existing talent.
Through Statistical research, researchers expect the global talent management software market to be about 16 billion USD by 2023, doubling approximately every four years.
How does a Talent Management System work?
The Talent Management system is a cloud-based platform that incorporates all the modules of the Human Resource department needed to find, search, attract, recruit, and develop employees in an organization.
This cloud platform delivers a range of benefits, including vast data storage capabilities, more robust security, and efficient integration with complementary applications like training programs, payroll, career planning, and other applications, and the sealed storage of employee data, for instance, demographics, personal information, and compensation. It helps HR professionals to select qualified candidates and drive the recruitment process more efficiently.
Capabilities of a Talent Management System:
Organizations can implement an end-to-end talent scheme while recruiting job applicants through TMS. This scheme will align with the goals and targets of the business. Three principal capabilities of TMS are:
- Recruitment: With TMS, finding, attracting, and hiring the best candidates becomes more effortless. These candidates, in turn, become high-performing employees, improving productivity and increasing organizational strength.
- Development: With TMS, organizations got the chance to build skills among the employees and adaptable teams to support and guide business performance. It will lead to robust and steady growth of the organization. Identifying and cultivating strong leaders also develops an organization.
- Retention: Help employees succeed in their professions, improving engagement and retention.
How to choose a Talent Management System?
When a workforce of an organization is looking for the best Talent Management software, they should make sure that they pick software that does what they need to improve their business growth. Secondly, they should opt for software that will integrate well with their technology, employees, and processes.
The talent management software one chooses should have the following capabilities:
- Performance and goals management
- Succession planning
- Recruitment functionality
- Reporting, Analytics
- Compensation
- Learning management
- Career and development planning
Some of the best talent management suites are as follows:
- ADP Workforce
- Talent Soft
- Deltek Human Capital Management
- Oracle HCM
- Talent Intelligence Platform (TIP)
- Cegid Talent Management
Who uses Talent Management System?
TMS is for every employee, including Human Resources professionals, recruiters, candidates, managers, and within an organization.
Why use a Talent Management System?
There are numerous reasons to use a Talent Management system. One of the most significant reasons is to optimize and automate the complete package of talent management processes within an organization. Some other reasons include owning top talent, capacity to hold a large amount of data, better hiring, shared data, promoting employee experience, and modern employee development.
Conclusion:
Every organization or company must quit using old and obsolete practices to respond to today's challenging talent market. So, they need to retain an efficient Talent Management System that helps them identify and recruit qualified talent. We hope this article has given an illustrative outlook on Talent Management systems (TMS).