Which compression types exist?
The following compression types exist:
| Compression type | M_CS_COLUMNS -> COMPRESSION_TYPE | Valid for | Details | Typical Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
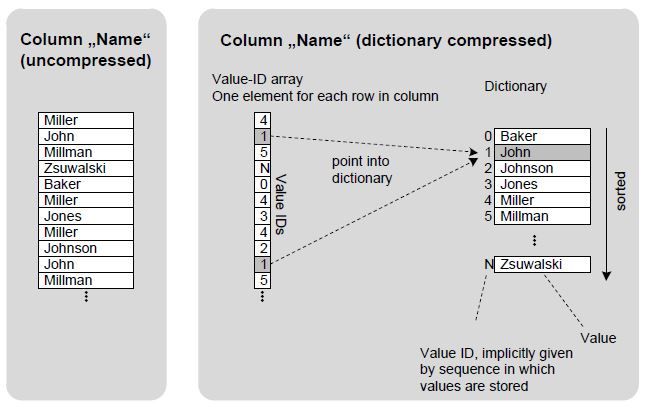
| Dictionary | DEFAULT | main delta | The standard column store dictionary approach already provides a significant space reduction, because the distinct column values are mapped to value ID numbers which typically require much less space in memory.Dictionary compression is always used. Additionally any one of the other compression techniques mentioned below can be in place. | generally |
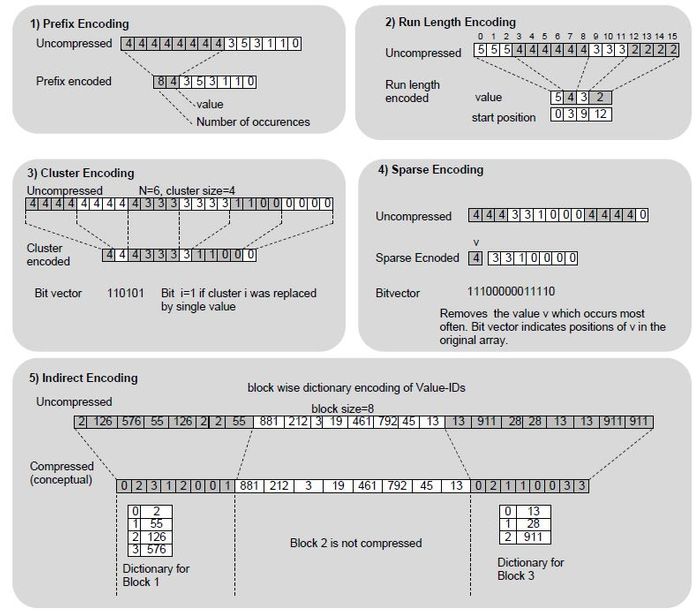
| Prefix encoding | PREFIXED | main | Identical values at the beginning of the value ID array are stored only once, together with the number of occurrences. | single predominant column value |
| Run-length encoding | RLE | main | Consecutive identical value IDs are replaced with a single instance of this value ID and its start position. | several frequent column values |
| Cluster encoding | CLUSTERED | main | The value ID array is cut into clusters of 1024 elements. If a cluster contains only occurrences of a single value, the cluster is replaced by a single occurrence of that value. | several frequent column values |
| Indirect encoding | INDIRECT | main | The value ID array is cut into clusters of 1024 elements. If a cluster contains only a few distinct value IDs, a cluster specific dictionary is created, so that each value ID is represented with even fewer bits. | several frequent column values |
| Sparse encoding | SPARSE | main | The most popular value is removed from the value ID array. A bit vector indicates at which positions the value was removed. | single predominant column value, value ID array not well clustered |
Additionally there is a compression of consecutive string values in the dictionary done ("delta compression"). It can't be influenced and so it is not discussed in detail at this point.
Read more about SAP HANA Security
The following pictures illustrate the different types of compression.
Dictionary compression:
Other compression types: