The world of retail is extremely dynamic. With ever-changing market trends and customer demands, retail companies always have to be equipped to handle them. They have to alter their business processes and strategies to deliver better customer solutions. So, retail companies require a software solution that synchronizes their supply chain, marketing, merchandising, and IT. This way, they can gain a competitive edge over their competitors.
This is where SAP IS Retail comes in. SAP IS Retail supports different assortment strategies, sales technologies, and offers enhanced logistics. We will learn more about the software product in detail in this article.
What is SAP Retail?
SAP IS Retail is a completely integrated ERP solution aimed at the retail industry. The software works well for small, medium, and large scale corporations. It aims to fully integrate all departments of a retail organization. These can be supply chain, marketing, and logistic departments. For a retail company, SAP IS Retail offers all the functions required to model business processes.
Features of SAP IS-Retail
Some of the salient features of SAP IS Retail are –
- Allows companies to collect and analyze statistical data
- The Purchasing functionality lets companies in vendor settlement and merchandise procurement
- It supports the sales processes such as customer order management, assortment planning, price planning, promotions, and store management
- It has interfaces that offer distributed data processing
- Companies can plan their sales strategies and price margins based on the current price reductions/fluctuations
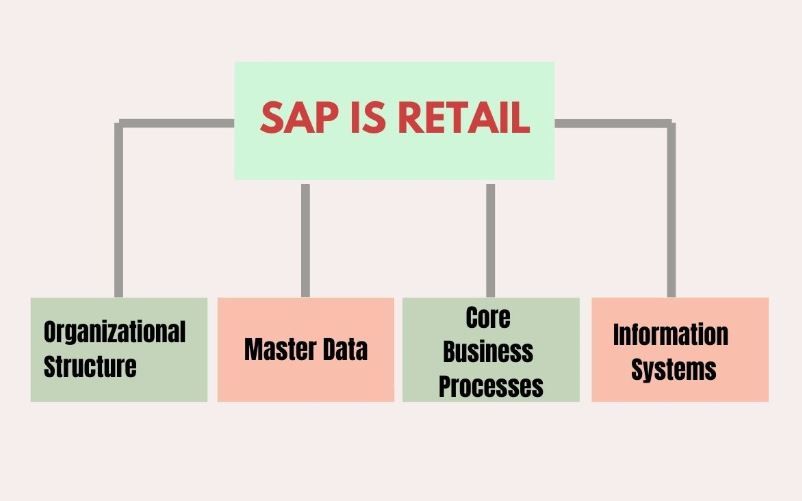
SAP IS Retail Components
The major components of SAP Retail are –
- Organizational Structure
- Master Data
- Core Business Processes
- Information Systems
1. Organizational Structure
This defines a company’s enterprise structure. Some of the most important units of this structure are –
- Company code – This is an accounting unit that represents the company. These codes are important to exchange goods between two firms
- Sales organization – This is a logistical organizational unit that is used while handling customer claims, distribution of goods, and price negotiation
- Distribution channel – A channel through which goods and services reach the end-users
Other units include storage location, controlling area, purchasing group, division, and shipping point.
2. Master Data
Master data is the foundational unit of business operations in retail. It is used for integrating business processes across different channels. The relationship between a vendor and the company is stored as master data. This is also the key component in transaction processing. Important components of master data are –
- Article master
- Site master
- Merchandise Category Master
- European Article Management
- Customer master data
- Vendor master data
- Merchandise hierarchy
Let us now understand some of these components.
i) Article Master
Article master consists of the information regarding a company’s goods or materials. This includes information about the materials stored, manufactured, and sold.
Merchandise Category and Merchandise Category Hierarchy
The merchandise category is a way of grouping goods of a company. The goods are classified based on their features. A merchandise category hierarchy is a group of Merchandise categories.
ii) Vendor Master
The vendor master database contains data about a company’s vendors. Individual vendor master records store this information. It has the following data –
- Vendors name and address
- Currency used while ordering from the vendor
- Payment terms
- Names of sales staff
iii) Customer Master
This can be considered as a function that is used for developing master data for new customers. It is also used to display or modify the existing customer master record data.
iv) Classification
Classification is used for grouping different entities having similar features together. These entities can be merchandise distribution and merchandize assortment planning.
v) Assortment
An assortment specifies whether a store, a customer or a distribution center can receive certain articles at a certain period. An article is the central object is retail logistics processes.
3. Core Business Processes
Companies determine their merchandise requirement based on current market trends and customer demands. After this, a purchase order is created for the vendor. Based on this order, the vendor delivers the merchandise, and the entire process is stored in the system. As a result of this process, the inventory at the distribution center increases. The inventory value is also enhanced.
Then the vendor sends invoices for the delivery of merchandise. These invoices are verified and rebates or discounts are applied to them. The company sends the final payment to the vendor.
In the retail industry, establishing a strong relationship between a company and a vendor takes time. Quotations are not requested straight away. But during the procurement of valuable articles and bulk goods, a company may need a price quotation. SAP IS Retail also allows companies to request quotations during this procurement process.
4. Information System
This is used for collecting and analyzing retail data. This data is fetched from different business processes such as inventory, sales, or purchasing.
SAP IS Retailing Process
The key retailing processes include –
- Assortment Management
- Calculating sales costs and prices
- Managing promotion of goods and services
- Allocation
- Purchasing and requirements Planning
- Goods Receipt
- Invoice Verification
- Settlement of End-Of-Period Arrangements
- Warehouse Management
- Pick-up and Delivery
- Billing
- Store Supply
All the retailing processes mentioned above allow companies to manage and control their value chain. The SAP IS Retail also helps them in attending to changing customer demands. It also helps in understanding future consumer needs. Changes to laws and business practices relating to the industry are also accommodated by SAP IS Retail.
The retailing processes help the organizations incorporate changes into their business processes smoothly.
Conclusion
SAP IS Retail has helped many retail companies enhance their business processes and revenue. It has completely changed the traditional retail strategies. Using SAP IS Retail, companies can now increase their customer engagement. Plus, its data processing functionalities have enabled companies to make better business decisions.